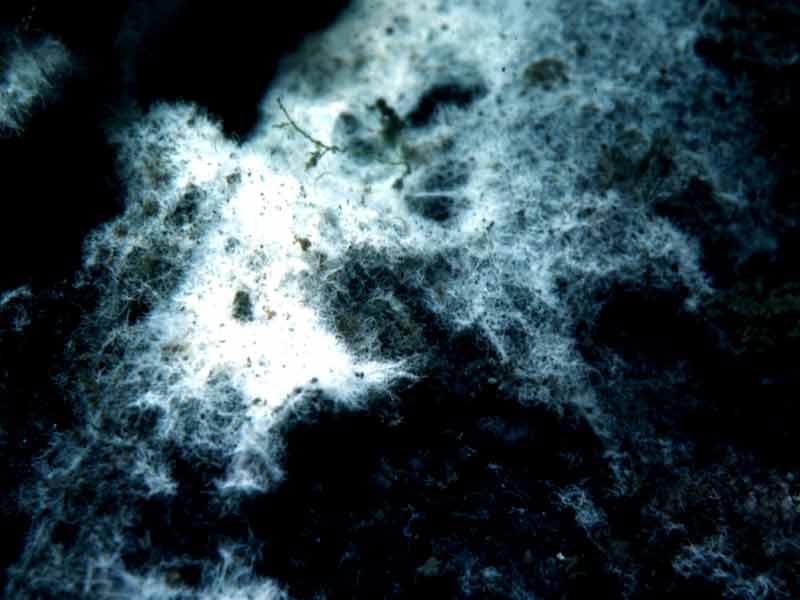
Beggiatoa spp. on anoxic sublittoral mud
| Researched by | Jacqueline Hill & Dr Harvey Tyler-Walters & Dr Samantha Garrard | Refereed by | This information is not refereed |
|---|
Summary
UK and Ireland classification
Description
Sublittoral soft anoxic mud, often in areas with poor water exchange with the open sea, can have a conspicuous bacterial mat covering of Beggiatoa species. The anoxia may be a result of natural conditions of poor water exchange in some sea lochs (and many Scandinavian fjords) or artificially under fish farm cages from nutrient enrichment. The fauna is normally impoverished at such sites, with few elements of the infaunal communities present in other muddy biotopes. Scavenging species such as Asterias rubens and Carcinus maenas are typically present where the habitat is not too anoxic but in extreme conditions of anoxia little survives other than the Beggiatoa. The polychaete Ophiodromus flexuosus occurs in high densities at the interface between oxygenated and deoxygenated sediments (in Norwegian fjords). (Information taken from the Marine Biotope Classification for Britain and Ireland, Version 97.06: Connor et al., 1997a, 2004).
Depth range
0-5 m, 5-10 m, 10-20 mAdditional information
None entered
Listed By
Habitat review
Ecology
Ecological and functional relationships
Mats of the sulphur reducing, filamentous bacteria Beggiatoa spp. occur at sites of organic pollution, often in areas of soft anoxic mud where there is poor water exchange with the open sea. Beggiatoa mats occur on the surface of the sediment at the hypoxic/anoxic interface. Beggiatoa sp. are characterized by their gliding motility, lack of photosynthetic pigments, and the presence of sulphur globules around the cytoplasm (Hagen & Nelson, 1997). The underlying sediment is primarily depauperate, the low oxygen levels resulting in death or loss of most mega and macrofauna. A few tolerant polychaetes, gastrotrichs, and nematodes may occur (e.g. see Bernhard et al., 2000). The Beggiatoa excludes other heterotrophic bacteria and most other macrofauna with few elements of the infaunal communities that are found in other muddy biotopes.
Beggiatoa sp. utilize sulphides leaching from the sediment, and oxidize them to sulphate to liberate energy for growth but also require simple organic acids and alcohols for growth (Williams & Unz, 1989; Hagen & Nelson, 1997).The other organisms present (e.g. ciliates, nematodes, and euglenoid flagellates) are probably decomposers, feeding on organic matter. However, Bernhard et al. (2000) noted several species of protist contained symbiotic bacteria that were presumably chemoautotrophs. The sediment below the mats is populated by chemoautotrophic bacteria, that remineralize organic matter, producing methane, or sulphides of hydrogen (H2S), iron or manganese and are probably very similar to microbial communities found at depth in other sediments (for a summary see Davies et al., 1996).
The few remaining tolerant species are probably deposit feeders on the microbial rich sediment or scavengers (e.g. crabs, hermit crabs, and starfish) feeding on dead or dying fauna.
Seasonal and longer term change
The development of Beggiatoa mats are related to environmental conditions such as organic input and oxygen content which may have seasonal trends in some areas. Anoxic conditions may also develop in deep water due to the presence of a thermocline in the summer months e.g. some Fjords (Diaz & Rosenberg, 1995; Gustafsson & Nordberg, 1999) and Aberiddy Quarry (Hiscock & Hoare, 1973).Habitat structure and complexity
The biotope has little structural complexity because the surface of the sediment is covered with a mat of the filamentous bacteria reducing access to sediments for infaunal organisms. Scavenging species such as Asterias rubens and Carcinus maenas are typically present where the habitat is not too anoxic but in extreme conditions of anoxia little survives other than the Beggiatoa. The polychaete Ophiodromus flexuosus occurs in high densities at the interface between oxygenated and deoxygenated sediments (in Norwegian fjords). The mats provide habitat for an abundant meiofaunal community (Bernhard et al., 2000) such as nematodes and small ciliates (Spies & Davis, 1979). The combination of anoxic conditions and the related production of sulphides (e.g. H2S) is highly toxic to most life (see Diaz & Rosenberg, 1995) and the underlying sediment may be effectively abiotic. Where conditions are not anoxic but severely hypoxic, Beggiatoa may be patchy, with an impoverished infauna present.Productivity
Productivity in this biotope is limited to the anaerobic chemoautotrophic productivity of infaunal bacteria and of the sulphur-oxidising bacteria Beggiatoa sp. Beggiatoa sp. utilize sulphides leaching from the sediment, and oxidize them to sulphate to liberate energy for growth but also require simple organic acids and alcohols for growth (Williams & Unz, 1989; Hagen & Nelson, 1997). Diaz & Rosenberg (1995) noted that area dominated by bacterial mats, the benthic-pelagic coupling is weakened and the food chain shortened. However, they also noted that bacterial mats may be important sources of organic matter in coastal upwelling oxygen minimum zones.Recruitment processes
Bacterial colonies can spread rapidly via asexual reproduction. In many species resting stages, spores and cysts may occur that allow some bacteria to survive for long periods returning to normal growth when conditions are good. Beggiatoa sp. are probably ubiquitous.Time for community to reach maturity
Although growth rates of Beggiatoa in natural environments are not known, the generation time for many bacteria is short and growth is usually exponential in optimal conditions (e.g. in some bacteria the population can double in 20 minutes). Therefore, in the right conditions, a Beggiatoa mat is likely to develop rapidly.Additional information
None entered.
Preferences & Distribution
Habitat preferences
| Depth Range | 0-5 m, 5-10 m, 10-20 m |
|---|---|
| Water clarity preferences | Not relevant |
| Limiting Nutrients | Not relevant |
| Salinity preferences | Full (30-40 psu), Variable (18-40 psu) |
| Physiographic preferences | |
| Biological zone preferences | Infralittoral |
| Substratum/habitat preferences | Mud |
| Tidal strength preferences | Very weak (negligible), Weak < 1 knot (<0.5 m/sec.) |
| Wave exposure preferences | Extremely sheltered, Sheltered, Very sheltered |
| Other preferences | High organic content, low oxygen and sulphides |
Additional Information
Mats of Beggiatoa spp. occur on the surface of organic rich, anoxic sediments, at the hypoxic/anoxic interface, and oxidize sulphides to sulphates. For example Bernhard et al. (2000) reported mats of Beggiatoa spp. on the surface of sediments at a depth of ca 600m, in which the oxygen concentration was < 1>0.1 µM.
Species composition
Species found especially in this biotope
- Beggiatoa sp.
Rare or scarce species associated with this biotope
-
Additional information
The MNCR recorded 149 species in records of this biotope. However, only scavenging Carcinus maenas and Asterias rubens were recorded as common. Numerous other species occur at low abundance or in only a few records of the biotope, probably reflecting the patchy nature of the Beggiatoa spp. mats.Sensitivity review
Sensitivity characteristics of the habitat and relevant characteristic species
This biotope is characterized by mats of the bacterium Beggiatoa spp. Since no or very few other macrofaunal species at least are present in the biotope the sensitivity of Beggiatoa is representative of the sensitivity of the whole biotope.
Resilience and recovery rates of habitat
Bacterial colonies can spread rapidly via asexual reproduction. In many species resting stages, spores and cysts may occur which allows some bacteria to survive for long periods returning to normal growth when conditions are good. Beggiatoa is probably ubiquitous. Jørgensen (1977) noted that Beggiatoa spp. was present in the upper few centimetres oxic sediment in Limfjorden, Denmark. It was absent from fine and medium sand but in mud occured at high densities around faecal pellets. Although growth rates of Beggiatoa are not known, the generation time for many bacteria is short (e.g. in some bacteria the population can double in 20 minutes). In the right conditions, a Beggiatoa mat is likely to develop very rapidly so that resilience is probably High (< 2 years).
Hydrological Pressures
Use [show more] / [show less] to open/close text displayed
| Resistance | Resilience | Sensitivity | |
Temperature increase (local) [Show more]Temperature increase (local)Benchmark. A 5°C increase in temperature for one month, or 2°C for one year. Further detail EvidenceBeggiatoa spp. mats have been reported from sulphur springs, deep water at ca 600 m, fjords, coastal marine sediments, salt marshes, organic-rich freshwater sediments, natural oil seeps and deep-sea hydrothermal vents (e.g. Spies & Davis, 1979; Hagen & Nelson, 1997). There was no information found regarding the temperature requirements of Beggiatoa, and the temperature requirements of individual strains of the bacterium are likely to vary. However, given its occurrence in the vicinity of hydrothermal vents, it is unlikely to be affected by increases in temperature at the benchmark level. In addition, Hiscock et al. (2001) suggested that increases in temperature because of global warming may result in more thermal stratification events in enclosed areas. Increased stratification will isolate deeper waters of sheltered sites and Beggiatoa spp. biotopes may occur where they did not previously exist. Therefore, resistance and resilience are probably High and the biotope is assessed as Not sensitive. | HighHelp | HighHelp | Not sensitiveHelp |
Temperature decrease (local) [Show more]Temperature decrease (local)Benchmark. A 5°C decrease in temperature for one month, or 2°C for one year. Further detail EvidenceBeggiatoa spp. mats have been reported from sulphur springs, deep water at ca 600 m, fjords, coastal marine sediments, salt marshes, organic-rich freshwater sediments, natural oil seeps and deep-sea hydrothermal vents (e.g. Spies & Davis, 1979; Hagen & Nelson, 1997). There was no information found regarding the temperature requirements of Beggiatoa, and the temperature requirements of individual strains of the bacterium are likely to vary. However, its occurrence within the East Siberian Sea (OBIS, 2016) and the deep sea suggest it is unlikely to be affected by increases in temperature at the benchmark level. Therefore, resistance and resilience are probably High and the biotope is assessed as Not sensitive. | HighHelp | HighHelp | Not sensitiveHelp |
Salinity increase (local) [Show more]Salinity increase (local)Benchmark. A increase in one MNCR salinity category above the usual range of the biotope or habitat. Further detail EvidenceThere is no information regarding the development of Beggiatoa mats in hypersaline waters. Freshwater strains and marine strains are different so an increase in salinity in brackish water sites may remove the freshwater strains of the bacterium, e.g. freshwater strains were unable to grow in salty conditions (Williams & Unz, 1989). However, if conditions of high nutrient and low oxygen concentration remain mats may then be formed by marine strains. Therefore, a resistance of High is suggested but with low confidence. Hence, resilience is High and the biotope is assessed as Not sensitive. | HighHelp | HighHelp | Not sensitiveHelp |
Salinity decrease (local) [Show more]Salinity decrease (local)Benchmark. A decrease in one MNCR salinity category above the usual range of the biotope or habitat. Further detail EvidenceBeggiatoa mats form in sewage waste water and in marine conditions. However, freshwater strains and marine strains are different so a decrease in salinity may remove the marine strains. For example, freshwater strains were unable to grow in salty conditions (Williams & Unz, 1989). However, if conditions of high nutrient and low oxygen concentration remain mats may then be formed by freshwater strains. Therefore, a resistance of High is suggested but with low confidence. Hence, resilience is High and the biotope is assessed as Not sensitive. | HighHelp | HighHelp | Not sensitiveHelp |
Water flow (tidal current) changes (local) [Show more]Water flow (tidal current) changes (local)Benchmark. A change in peak mean spring bed flow velocity of between 0.1 m/s to 0.2 m/s for more than one year. Further detail EvidenceThe biotope normally develops in areas of low water flow rate, such as sea lochs and fjords, where hypoxic or anoxic conditions are able to develop. Any further decrease in water flow is unlikely and assessed further. An increase in water flow is likely to result in increased mixing of the water column, and dispersal of any thermocline or halocline in the area, an increase in oxygenation of the water column and loss of the conditions required for growth of Beggiatoa spp. In areas where anoxic or hypoxic conditions are caused by organic enrichment, then increased water flow is likely to mitigate and reduce the level of hypoxia. However, an increase of 0.1-0.2 m/s (the benchmark) may reduce the level of hypoxia in naturally hypoxic areas. Therefore, a resistance of Low is suggested but with Low confidence. Resilience is likely to be High so that sensitivity is assessed as Low. | LowHelp | HighHelp | LowHelp |
Emergence regime changes [Show more]Emergence regime changesBenchmark. 1) A change in the time covered or not covered by the sea for a period of ≥1 year or 2) an increase in relative sea level or decrease in high water level for ≥1 year. Further detail EvidenceThe pressure benchmark is relevant only to littoral and shallow sublittoral fringe biotopes. | Not relevant (NR)Help | Not relevant (NR)Help | Not relevant (NR)Help |
Wave exposure changes (local) [Show more]Wave exposure changes (local)Benchmark. A change in near shore significant wave height of >3% but <5% for more than one year. Further detail EvidenceThe biotope develops in areas of very little water movement (wave sheltered to extremely wave sheltered conditions). Therefore, a further decrease in wave action is unlikely. An increase in wave action is likely to wash the mats away and increase mixing or the water column and, hence, oxygenation. However, a 3-5% change in significant wave height is unlikely to have a significant effect, especially at depth. Therefore, resistance and resilience are probably High and the biotope is assessed as Not sensitive. | HighHelp | HighHelp | Not sensitiveHelp |
Chemical Pressures
Use [show more] / [show less] to open/close text displayed
| Resistance | Resilience | Sensitivity | |
Transition elements & organo-metal contamination [Show more]Transition elements & organo-metal contaminationBenchmark. Exposure of marine species or habitat to one or more relevant contaminants via uncontrolled releases or incidental spills. Further detail EvidenceThis pressure is Not assessed but evidence is presented where available. | Not Assessed (NA)Help | Not assessed (NA)Help | Not assessed (NA)Help |
Hydrocarbon & PAH contamination [Show more]Hydrocarbon & PAH contaminationBenchmark. Exposure of marine species or habitat to one or more relevant contaminants via uncontrolled releases or incidental spills. Further detail EvidenceIn many areas around the world (e.g. see Spies & Davis, 1979) mats of Beggiatoa are associated with localized intense oil seepage and so the biotope is likely to be relatively resistant of hydrocarbons. Nevertheless, this pressure is Not assessed . | Not Assessed (NA)Help | Not assessed (NA)Help | Not assessed (NA)Help |
Synthetic compound contamination [Show more]Synthetic compound contaminationBenchmark. Exposure of marine species or habitat to one or more relevant contaminants via uncontrolled releases or incidental spills. Further detail EvidenceThis pressure is Not assessed but evidence is presented where available. | Not Assessed (NA)Help | Not assessed (NA)Help | Not assessed (NA)Help |
Radionuclide contamination [Show more]Radionuclide contaminationBenchmark. An increase in 10µGy/h above background levels. Further detail EvidenceNo evidence was found. | No evidence (NEv)Help | Not relevant (NR)Help | No evidence (NEv)Help |
Introduction of other substances [Show more]Introduction of other substancesBenchmark. Exposure of marine species or habitat to one or more relevant contaminants via uncontrolled releases or incidental spills. Further detail EvidenceThis pressure is Not assessed. | Not Assessed (NA)Help | Not assessed (NA)Help | Not assessed (NA)Help |
De-oxygenation [Show more]De-oxygenationBenchmark. Exposure to dissolved oxygen concentration of less than or equal to 2 mg/l for one week (a change from WFD poor status to bad status). Further detail EvidenceJørgensen (1977) noted that Beggiatoa spp. was present in the upper few centimetres oxic sediment in Limfjorden, Denmark. But mats of Beggiatoa are usually associated with hypoxic or anoxic conditions (Diaz & Rosenberg, 1995; Connor et al., 1997a,2004). For example, during the autumn of 1993 and 1994 when the oxygen content of the bottom water in the Koljoford on the west coast of Sweden dropped, Beggiatoa mats covered the seafloor (Gustafsson & Nordberg, 1999). In Maine coastal waters in the U.S.A, the formation of Beggiatoa mats was linked to lack of oxygen when current speed was reduced for 2 h or longer during a tidal cycle. The formation of Beggiatoa mats only occurs when oxygen supply is reduced below the threshold level required to oxidize sedimented organic matter (Findlay, 2002). In Caol Scotnish, Loch Sween, bacterial mats of Beggiatoa were reported in the immediate vicinity of salmon cages in 1987. By 1988, the bacterial mats covered most of the seabed in the basin and the sediment was close to anoxic (Atkinson, 1989; Hughes, 1998a). Therefore, the development of the biotope is dependent on hypoxic and anoxic conditions in the sediment. The biotope is assessed as Not sensitive (resistance and resilience are High) to deoxygenation. However, the biotope would be destroyed and lost by increased oxygen levels. | HighHelp | HighHelp | Not sensitiveHelp |
Nutrient enrichment [Show more]Nutrient enrichmentBenchmark. Compliance with WFD criteria for good status. Further detail EvidenceMats of Beggiatoa are usually associated with and develop in the presence of high organic loadings such as found under salmon farm cages (Lumb, 1989; Davies et al., 1996, Atkinson, 1989) and coastal areas of eutrophication (Graco et al., 2001). Therefore, an increase in nutrients will encourage the development of the bacterial mats. The biotope is probably Not sensitive (resistance and resilience are High) to nutrient enrichment. Nevertheless, the biotope is assessed as Not sensitive at the pressure benchmark that assumes compliance with good status as defined by the WFD. | Not relevant (NR)Help | Not relevant (NR)Help | Not sensitiveHelp |
Organic enrichment [Show more]Organic enrichmentBenchmark. A deposit of 100 gC/m2/yr. Further detail EvidenceMats of Beggiatoa are usually associated with and develop in the presence of high organic loadings such as found under salmon farm cages (Lumb, 1989; Davies et al., 1996, Atkinson, 1989) and coastal areas of eutrophication (Graco et al., 2001). Therefore, an increase in nutrients will encourage the development of the bacterial mats. The biotope is assessed as Not sensitive (resistance and resilience are High) to organic enrichment. | HighHelp | HighHelp | Not sensitiveHelp |
Physical Pressures
Use [show more] / [show less] to open/close text displayed
| Resistance | Resilience | Sensitivity | |
Physical loss (to land or freshwater habitat) [Show more]Physical loss (to land or freshwater habitat)Benchmark. A permanent loss of existing saline habitat within the site. Further detail EvidenceAll marine habitats and benthic species are considered to have a resistance of ‘None’ to this pressure and to be unable to recover from a permanent loss of habitat (resilience is ‘Very Low’). Sensitivity within the direct spatial footprint of this pressure is, therefore ‘High’. Although no specific evidence is described confidence in this assessment is ‘High’, due to the incontrovertible nature of this pressure. | NoneHelp | Very LowHelp | HighHelp |
Physical change (to another seabed type) [Show more]Physical change (to another seabed type)Benchmark. Permanent change from sedimentary or soft rock substrata to hard rock or artificial substrata or vice-versa. Further detail EvidenceIf sedimentary substrata were replaced with rock substrata the biotope would be lost, as it would no longer be a sedimentary habitat as described under the habitat classification. Jørgensen (1977) noted that Beggiatoa was absent from fine and medium sands in the Limfjorden, Denmark but abundant on muds. Therefore, a change to rock substratum would probably result in loss of Beggiatoa mats. Sensitivity assessment. Resistance to the pressure is considered ’None‘, and resilience ’Very low‘ or ‘None’ (as the pressure represents a permanent change) and the sensitivity of this biotope is assessed as ’High’. | NoneHelp | Very LowHelp | HighHelp |
Physical change (to another sediment type) [Show more]Physical change (to another sediment type)Benchmark. Permanent change in one Folk class (based on UK SeaMap simplified classification). Further detail EvidenceBeggiatoa spp. is recorded from muds and decaying plant matter (Jørgensen, 1977). Jørgensen (1977) noted that Beggiatoa was absent from fine and medium sands in the Limfjorden, Denmark but abundant on muds. Similarly, this biotope (IFiMu.Beg) is only recorded from muds (Connor et al., 2004). Therefore, a change in sediment type by one Folk class (see Long, 2006), e.g. from mud to sandy mud and sand would result in loss of the biotope. Therefore, a resistance of None is recorded. As the change is permanent, resilience is Very low and sensitivity is assessed as High. | NoneHelp | Very LowHelp | HighHelp |
Habitat structure changes - removal of substratum (extraction) [Show more]Habitat structure changes - removal of substratum (extraction)Benchmark. The extraction of substratum to 30 cm (where substratum includes sediments and soft rock but excludes hard bedrock). Further detail EvidenceThe mats of Beggiatoa spp. sit on the surface of the substratum. Extraction of sediment to 30 cm (the benchmark) could remove the bacterial mats in the affected area. Hence, the resistance is probably None and resilience is probably High, resulting in a sensitivity of Medium. | NoneHelp | HighHelp | MediumHelp |
Abrasion / disturbance of the surface of the substratum or seabed [Show more]Abrasion / disturbance of the surface of the substratum or seabedBenchmark. Damage to surface features (e.g. species and physical structures within the habitat). Further detail EvidenceThe bacteria produces a polysaccharide matrix that binds the bacteria together and to the substratum. But mats of Beggiatoa form on soft mud and so are likely to be broken up by abrasion or physical disturbance. Therefore, a resistance of Low is suggested with Low confidence. However, resilience is probably High so that the sensitivity is assessed as Low. | LowHelp | HighHelp | LowHelp |
Penetration or disturbance of the substratum subsurface [Show more]Penetration or disturbance of the substratum subsurfaceBenchmark. Damage to sub-surface features (e.g. species and physical structures within the habitat). Further detail EvidenceThe bacteria produces a polysaccharide matrix that binds the bacteria together and to the substratum. But mats of Beggiatoa form on soft mud and so are likely to be broken up by abrasion or physical disturbance. Therefore, a resistance of Low is suggested with Low confidence. However, resilience is probably High so that the sensitivity is assessed as Low. | LowHelp | HighHelp | LowHelp |
Changes in suspended solids (water clarity) [Show more]Changes in suspended solids (water clarity)Benchmark. A change in one rank on the WFD (Water Framework Directive) scale e.g. from clear to intermediate for one year. Further detail EvidenceBeggiatoa spp. has no dependency on light or detritus, and no feeding structures to clog with sediment. This biotope is recorded from sheltered areas, on fine sediments, subject to high suspended sediment loads. Therefore, resistance is probably High and, hence, resilience is also High, and the biotope is probably Not sensitive at the benchmark level. | HighHelp | HighHelp | Not sensitiveHelp |
Smothering and siltation rate changes (light) [Show more]Smothering and siltation rate changes (light)Benchmark. ‘Light’ deposition of up to 5 cm of fine material added to the seabed in a single discrete event. Further detail EvidenceBeggiatoa spp. sit at the anoxia / hypoxia interface and can ‘glide’ across the surface of the substratum. It occurs in muds in sheltered areas and is probably adapted to high sediment loads and accretion rates. However, no information on rapid sedimentation was found. The bacterium is found within the top few centimetres of the sediment (Jørgensen, 1977) so that the bacterium itself would probably survive smothering but the mats would probably disappear temporarily. Therefore, a resistance of Low is suggested with Low confidence but resilience is High so that the sensitivity is assessed as Low. | LowHelp | HighHelp | LowHelp |
Smothering and siltation rate changes (heavy) [Show more]Smothering and siltation rate changes (heavy)Benchmark. ‘Heavy’ deposition of up to 30 cm of fine material added to the seabed in a single discrete event. Further detail EvidenceBeggiatoa spp. sit at the anoxia / hypoxia interface and can ‘glide’ across the surface of the substratum. It occurs in muds in sheltered areas and is probably adapted to high sediment loads and accretion rates. However, no information on rapid sedimentation was found. The bacterium is found within the top few centimetres of the sediment (Jørgensen, 1977) so that the bacterium itself would probably survive smothering but the mats would probably disappear temporarily. Therefore, a resistance of Low is suggested with Low confidence but resilience is High so that the sensitivity is assessed as Low. | LowHelp | HighHelp | LowHelp |
Litter [Show more]LitterBenchmark. The introduction of man-made objects able to cause physical harm (surface, water column, seafloor or strandline). Further detail EvidenceNot assessed. | Not Assessed (NA)Help | Not assessed (NA)Help | Not assessed (NA)Help |
Electromagnetic changes [Show more]Electromagnetic changesBenchmark. A local electric field of 1 V/m or a local magnetic field of 10 µT. Further detail EvidenceNo evidence was found | No evidence (NEv)Help | Not relevant (NR)Help | No evidence (NEv)Help |
Underwater noise changes [Show more]Underwater noise changesBenchmark. MSFD indicator levels (SEL or peak SPL) exceeded for 20% of days in a calendar year. Further detail EvidenceMotile bacteria may respond to local vibration but the important characteristic species are unlikely to respond to noise as described under this pressure. | Not relevant (NR)Help | Not relevant (NR)Help | Not relevant (NR)Help |
Introduction of light or shading [Show more]Introduction of light or shadingBenchmark. A change in incident light via anthropogenic means. Further detail EvidenceBeggiatoa sp. utilize sulphides leaching from the sediment, and oxidize them to sulphate to liberate energy for growth but also require simple organic acids and alcohols for growth (Williams & Unz, 1989; Hagen & Nelson, 1997).The other organisms present (e.g. ciliates, nematodes, and euglenoid flagellates) are probably decomposers, feeding on organic matter. However, Bernhard et al. (2000) noted several species of protist contained symbiotic bacteria that were presumably chemoautotrophs. The sediment below the mats is populated by chemoautotrophic bacteria, that remineralize organic matter, producing methane, or sulphides of hydrogen (H2S), iron or manganese and are probably very similar to microbial communities found at depth in other sediments (for a summary see Davies et al., 1996). Therefore, the biotope has not dependency on light and resistance is assessed as High. Therefore, resilience is High and the biotope is assessed as Not sensitive. | HighHelp | HighHelp | Not sensitiveHelp |
Barrier to species movement [Show more]Barrier to species movementBenchmark. A permanent or temporary barrier to species movement over ≥50% of water body width or a 10% change in tidal excursion. Further detail EvidenceNot relevant - this pressure is considered applicable to mobile species, e.g. fish and marine mammals rather than seabed habitats. Physical and hydrographic barriers may limit the dispersal of seed. But seed dispersal is not considered under the pressure definition and benchmark. | Not relevant (NR)Help | Not relevant (NR)Help | Not relevant (NR)Help |
Death or injury by collision [Show more]Death or injury by collisionBenchmark. Injury or mortality from collisions of biota with both static or moving structures due to 0.1% of tidal volume on an average tide, passing through an artificial structure. Further detail EvidenceNot relevant to seabed habitats. | Not relevant (NR)Help | Not relevant (NR)Help | Not relevant (NR)Help |
Visual disturbance [Show more]Visual disturbanceBenchmark. The daily duration of transient visual cues exceeds 10% of the period of site occupancy by the feature. Further detail EvidenceNot relevant | Not relevant (NR)Help | Not relevant (NR)Help | Not relevant (NR)Help |
Biological Pressures
Use [show more] / [show less] to open/close text displayed
| Resistance | Resilience | Sensitivity | |
Genetic modification & translocation of indigenous species [Show more]Genetic modification & translocation of indigenous speciesBenchmark. Translocation of indigenous species or the introduction of genetically modified or genetically different populations of indigenous species that may result in changes in the genetic structure of local populations, hybridization, or change in community structure. Further detail EvidenceNo evidence of genetic modification, breeding, or translocation was found. | No evidence (NEv)Help | Not relevant (NR)Help | No evidence (NEv)Help |
Introduction of microbial pathogens [Show more]Introduction of microbial pathogensBenchmark. The introduction of relevant microbial pathogens or metazoan disease vectors to an area where they are currently not present (e.g. Martelia refringens and Bonamia, Avian influenza virus, viral Haemorrhagic Septicaemia virus). Further detail EvidenceNo evidence was found. | No evidence (NEv)Help | Not relevant (NR)Help | No evidence (NEv)Help |
Removal of target species [Show more]Removal of target speciesBenchmark. Removal of species targeted by fishery, shellfishery or harvesting at a commercial or recreational scale. Further detail EvidenceBeggiatoa spp. are unlikely to be targeted by commercial or recreational fisheries or other harvest. The presence of mats of Beggiatoa spp. indicate that conditions are anoxic and potentially abiotic. | Not relevant (NR)Help | Not relevant (NR)Help | Not relevant (NR)Help |
Removal of non-target species [Show more]Removal of non-target speciesBenchmark. Removal of features or incidental non-targeted catch (by-catch) through targeted fishery, shellfishery or harvesting at a commercial or recreational scale. Further detail EvidenceThe presence of mats of Beggiatoa spp. indicate that conditions are anoxic and potentially abiotic. Affected areas are unlikely to be targeted by commercial or recreational fisheries or other harvest. | Not relevant (NR)Help | Not relevant (NR)Help | Not relevant (NR)Help |
Introduction or spread of invasive non-indigenous species (INIS) Pressures
Use [show more] / [show less] to open/close text displayed
| Resistance | Resilience | Sensitivity | |
Other INIS [Show more]Other INISEvidenceNo evidence was found. | No evidence (NEv)Help | Not relevant (NR)Help | No evidence (NEv)Help |
Bibliography
Atkinson, R.J.A., 1989. Baseline survey of the burrowing megafauna of Loch Sween, proposed Marine Nature Reserve, and an investigation of the effects of trawling on the benthic megafauna. Report to the Nature Conservancy Council, Peterborough, from the University Marine Biological Station, Millport, pp.1-59.
Bernhard, J.M., Buck, K.R., Farmer, M.A. & Bowser, S.S., 2000. The Santa Barbara Basin is a symbiosis oasis. Nature, 403, 77-80.
Connor, D.W., Allen, J.H., Golding, N., Howell, K.L., Lieberknecht, L.M., Northen, K.O. & Reker, J.B., 2004. The Marine Habitat Classification for Britain and Ireland. Version 04.05. ISBN 1 861 07561 8. In JNCC (2015), The Marine Habitat Classification for Britain and Ireland Version 15.03. [2019-07-24]. Joint Nature Conservation Committee, Peterborough. Available from https://mhc.jncc.gov.uk/
Connor, D.W., Dalkin, M.J., Hill, T.O., Holt, R.H.F. & Sanderson, W.G., 1997a. Marine biotope classification for Britain and Ireland. Vol. 2. Sublittoral biotopes. Joint Nature Conservation Committee, Peterborough, JNCC Report no. 230, Version 97.06., Joint Nature Conservation Committee, Peterborough, JNCC Report no. 230, Version 97.06.
Davies, I.M., Smith, P., Nickell, T.D. & Provost, P.G., 1996. Interactions of salmon farming and benthic microbiology in sea lochs. In Aquaculture and sea lochs (ed. K.D. Black), pp. 33-39., Oban: Scottish Association for Marine Science
Diaz, R.J. & Rosenberg, R., 1995. Marine benthic hypoxia: a review of its ecological effects and the behavioural responses of benthic macrofauna. Oceanography and Marine Biology: an Annual Review, 33, 245-303.
Findlay, R.H., 2002. Test of a model that predicts benthic impact of salmon net pen aquaculture. http://www.mar.dfo-mpo.gc.ca/science/mesd/he/eim/papers/findlay.html, 2026-04-02
Graco, M., Farias, L., Molina, V., Gutierrez, D. & Nielsen, L.P. 2001. Massive developments of microbial mats following phytoplankton blooms in a naturally eutrophic bay: Implications for nitrogen cycling. Limnology and Oceanography, 46, 821-832.
Gustafsson, M. & Nordberg, K., 1999. Benthic foraminifera and their response to hydrography, periodic hypoxic conditions and primary production in the Koljo fjord on the Swedish west coast. Journal of Sea Research, 41, 163-178.
Hagen, K.D. & Nelson, D.C., 1997. Use of reduced sulfur compounds by Beggiatoa spp.: enzymology and physiology of marine and freshwater strains in homogeneous and gradient cultures. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 63, 3957-3964.
Hiscock, K., Southward, A., Tittley, I., Jory, A. & Hawkins, S., 2001. The impact of climate change on subtidal and intertidal benthic species in Scotland. Scottish National Heritage Research, Survey and Monitoring Report , no. 182., Edinburgh: Scottish National Heritage
Hughes, D.J., 1998a. Sea pens & burrowing megafauna (volume III). An overview of dynamics and sensitivity characteristics for conservation management of marine SACs. Natura 2000 report prepared for Scottish Association of Marine Science (SAMS) for the UK Marine SACs Project., Scottish Association for Marine Science. (UK Marine SACs Project). Available from: http://ukmpa.marinebiodiversity.org/uk_sacs/pdfs/seapens.pdf
Jørgensen, B. B., 1977. Distribution of colorless sulfur bacteria (Beggiatoa spp.) in a coastal marine sediment. Marine Biology, 41(1), 19-28.
JNCC (Joint Nature Conservation Committee), 2022. The Marine Habitat Classification for Britain and Ireland Version 22.04. [Date accessed]. Available from: https://mhc.jncc.gov.uk/
JNCC (Joint Nature Conservation Committee), 1999. Marine Environment Resource Mapping And Information Database (MERMAID): Marine Nature Conservation Review Survey Database. [on-line] http://www.jncc.gov.uk/mermaid
Lumb, C.M., 1989. Self-pollution by Scottish salmon farms? Marine Pollution Bulletin, 20, 375-379.
OBIS, 2016. Ocean Biogeographic Information System (OBIS). http://www.iobis.org, 2016-03-15
Spies, R.B. & Davis, P., 1979. The infaunal benthos of a natural oil seep in the Santa Barbara Channel. Marine Biology, 50, 227-237.
Williams, T.M & Unz, R.F., 1989. The nutrition of Thiothrix, Type 021N, Beggiatoa and Leucothrix strains. Water Research, 23, 15-22.
Citation
This review can be cited as:
Last Updated: 31/05/2016