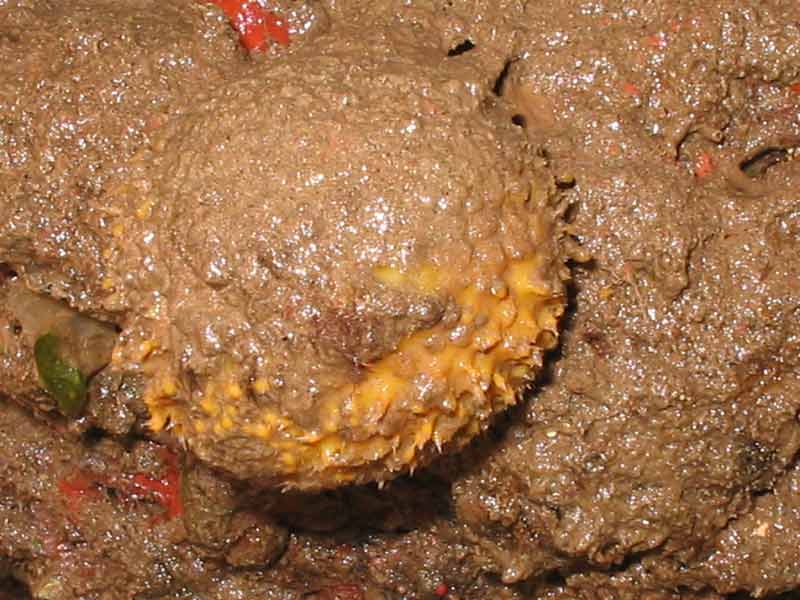
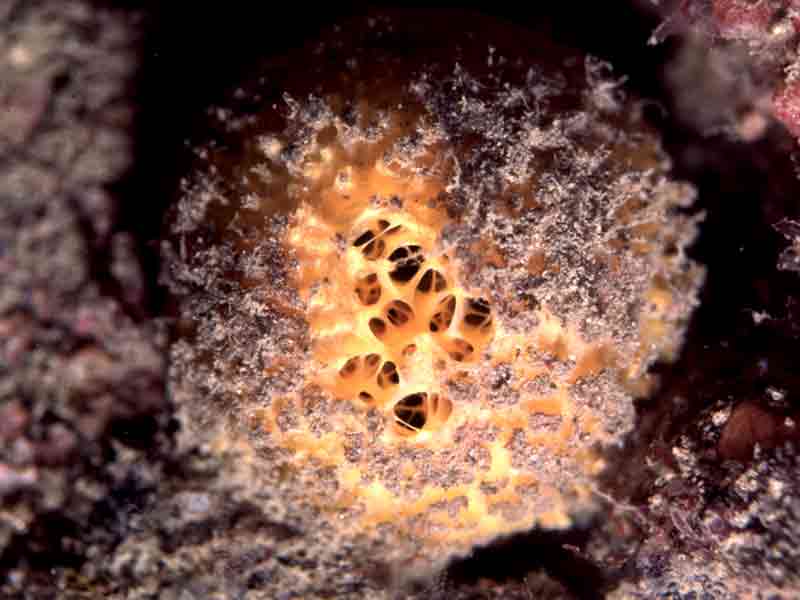
Golf ball sponge (Tethya aurantium)
Distribution data supplied by the Ocean Biodiversity Information System (OBIS). To interrogate UK data visit the NBN Atlas.Map Help
| Researched by | Judith Oakley | Refereed by | Admin |
| Authority | (Pallas, 1766) | ||
| Other common names | - | Synonyms | - |
Summary
Description
Recorded distribution in Britain and Ireland
Recorded from south-west England, the west coast of Wales, western Scotland and most Irish coasts, excluding the east.Global distribution
Recorded from Norway to the Mediterranean and from New Zealand.Habitat
Tethya aurantium grows singly or in colonies on rocks, boulders and stones in the shallow sublittoral to depths of 130 m. It is often found on rocks in kelp forests.Depth range
-Identifying features
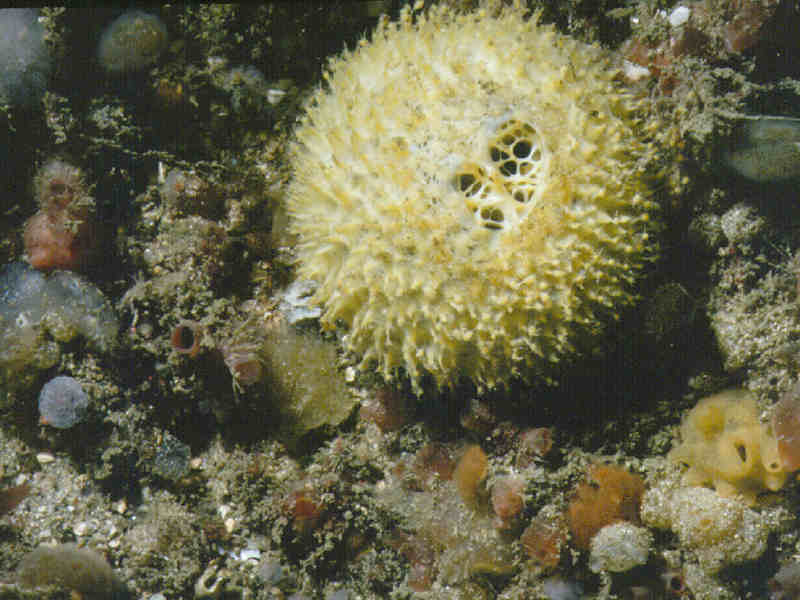
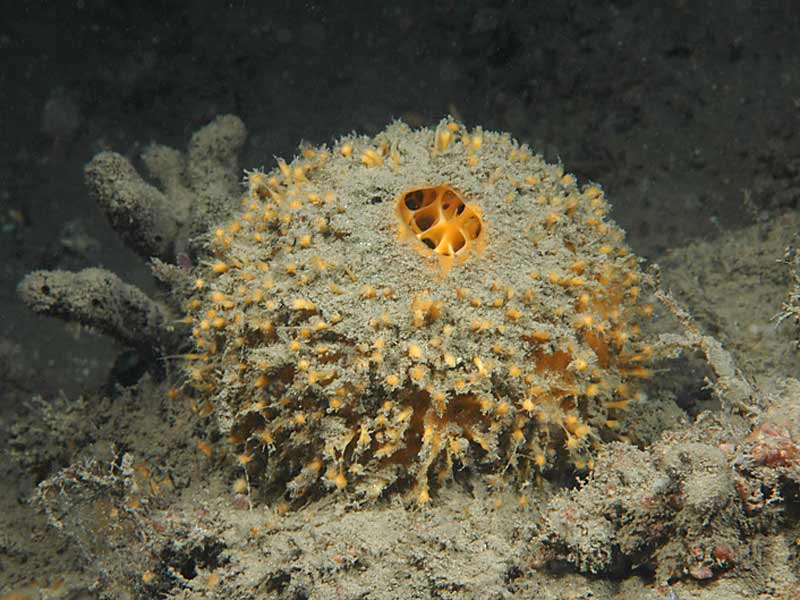
- Spherical/hemispherical.
- Usually yellow or orange.
- Up to 10 cm diameter.
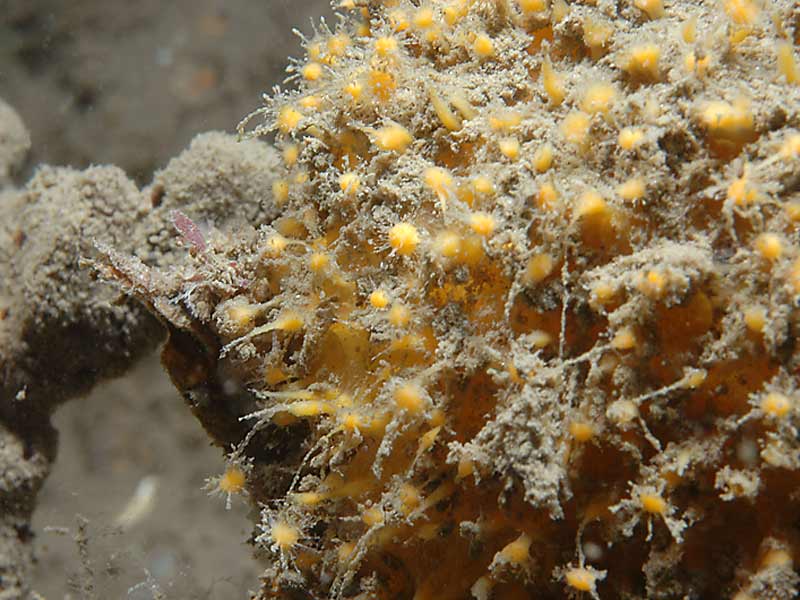
- Surface tuberculate or warty.
- Often covered by a layer of silt.
- Usually one large and distinct apical osculum.
- The sphere has a short basal stalk which grows from a root-like mass.
Additional information
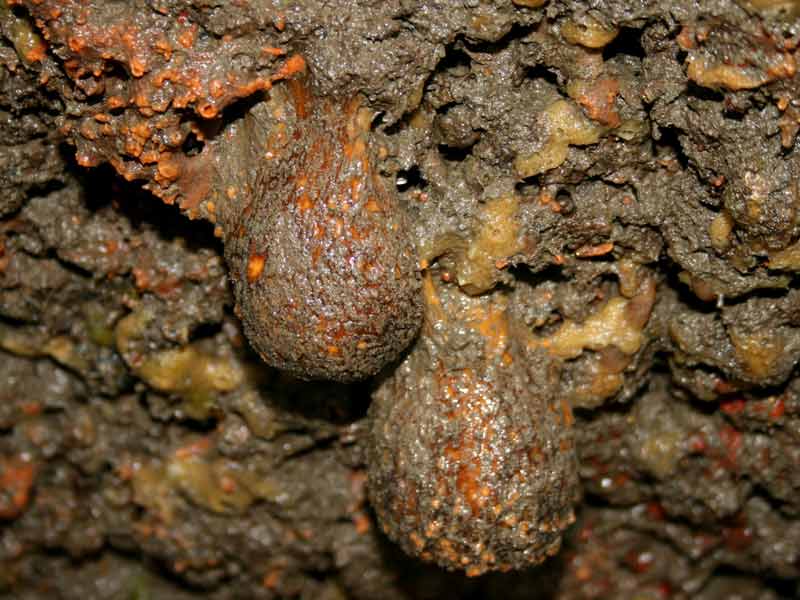
Stalked reproductive buds are produced between July and September (van Soest et al., 2000).Listed by
- none -
Bibliography
Gibson, R., Hextall, B. & Rogers, A., 2001. Photographic guide to the sea and seashore life of Britain and north-west Europe. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Howson, C.M. & Picton, B.E. ed., 1999. The species directory of the marine fauna and flora of the British Isles and surrounding seas. CD-ROM Edition. Ulster Museum and The Marine Conservation Society, Belfast and Ross-on-Wye., Belfast: Ulster Museum. [Ulster Museum publication no. 280.]
JNCC (Joint Nature Conservation Committee), 1999. Marine Environment Resource Mapping And Information Database (MERMAID): Marine Nature Conservation Review Survey Database. [on-line] http://www.jncc.gov.uk/mermaid
MarLIN (Marine Life Information Network), 2005. SEArchable BEnthic Data (SEABED) Map [on-line]. Data Access Sub-programme, Marine Life Information Network for Britian and Ireland http://www.marlin.ac.uk,
Moss, D., & Ackers, G. (eds.), 1982. The UCS Sponge Guide. Produced by R. Earll. Ross-on-Wye: The Underwater Conservation Society.
Picton, B.E. & Costello, M.J., 1998. BioMar biotope viewer: a guide to marine habitats, fauna and flora of Britain and Ireland. [CD-ROM] Environmental Sciences Unit, Trinity College, Dublin.
Van Soest, R.W.M., Picton, B. & Morrow, C., 2000. Sponges of the North East Atlantic. [CD-ROM] Windows version 1.0. Amsterdam: Biodiversity Center of ETI, Multimedia Interactive Software. [World Biodiversity Database CD-ROM Series.]
Datasets
Centre for Environmental Data and Recording, 2018. Ulster Museum Marine Surveys of Northern Ireland Coastal Waters. Occurrence dataset https://www.nmni.com/CEDaR/CEDaR-Centre-for-Environmental-Data-and-Recording.aspx accessed via NBNAtlas.org on 2018-09-25.
Manx Biological Recording Partnership, 2022. Isle of Man historical wildlife records 1990 to 1994. Occurrence dataset:https://doi.org/10.15468/aru16v accessed via GBIF.org on 2024-09-27.
NBN (National Biodiversity Network) Atlas. Available from: https://www.nbnatlas.org.
OBIS (Ocean Biodiversity Information System), 2025. Global map of species distribution using gridded data. Available from: Ocean Biogeographic Information System. www.iobis.org. Accessed: 2025-07-31
South East Wales Biodiversity Records Centre, 2023. SEWBReC Marine and other Aquatic Invertebrates (South East Wales). Occurrence dataset:https://doi.org/10.15468/zxy1n6 accessed via GBIF.org on 2024-09-27.
Citation
This review can be cited as:
Last Updated: 08/05/2008